Versioning
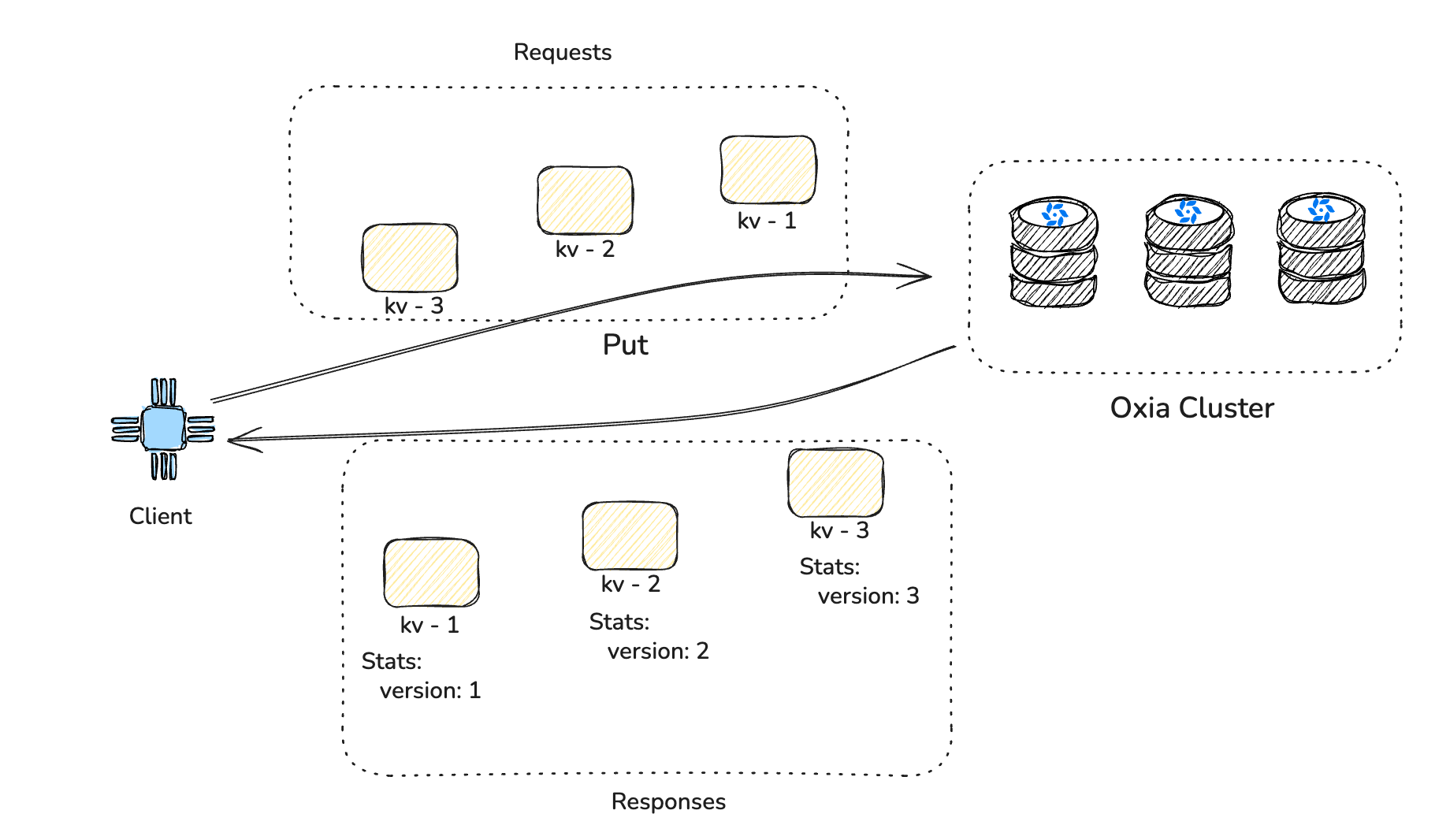
Oxia will assign a version to all mutable operations.
Therefore, you can use this assigned version as the expected value for subsequent mutable operations to support CompareThenSet-like atomic operations.
Use cases
The versioning is usually used for Optimistic Concurrency Control (OCC). Instead of locking resources, each item has a version number. When you read an item, you get its version. When you try to update it, you send back the version you read. If the version on the server doesn’t match, it means someone else updated the item in the interim, and your put fails. You then typically retry the operation by re-reading the latest version.
Using Versioning
Go
// read version
key, value, version, err := client.Get(context.Background(), "/my-key")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// case-1: expect not exists
_, res1, err := client.Put(context.Background(), "/my-key", []byte("value-1"), ExpectedRecordNotExists())
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// case-2: expect by version
_, _, err = client.Put(context.Background(), "/my-key", []byte("value-2"), ExpectedVersionId(version))
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}Last updated on